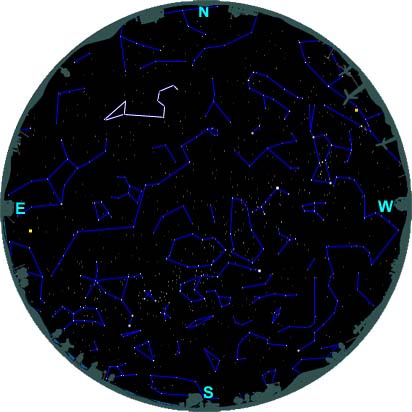
Leo Constellation Facts

Highlighted in yellow is the asterism which forms the head of Leo, known as 'The Sickle'.
- Leo contains several bright stars making it one the most easily recognizable constellations in the night sky.
- The constellation is visible in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
- In the Northern hemisphere the constellation can be seen from January to June.
- The stars that make up the bowl of the 'Big Dipper' asterism point towards the constellation in the Northern hemisphere.
- In the Southern hemisphere Leo can be viewed in the summer and autumn months.
- In the Southern hemisphere Leo will appear upside down.
- The brightest star in the constellation is Regulus, which has surface temperatures more than twice that of the sun.
- The Latin word for lion is leo.
- Leo is one of the oldest recorded constellations, it was perceived as a lion by ancient civilizations as far back as 6,000 years ago.
- Leo is also one of the twelve signs of the zodiac.
Leo Mythology

The constellation of Leo was recognized as a lion by several ancient civilizations.
Main Stars in the Leo Constellation
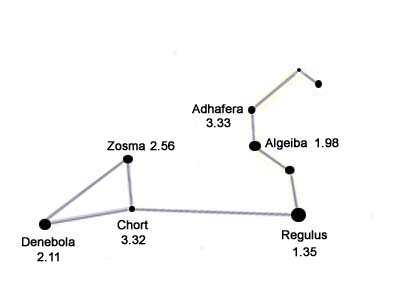
The number next to each star is its apparent magnitude, its brightness from our point of view
on Earth, the lower the number the brighter the star in the night sky.
Also known as Beta Leonis, Denebola is a bright white main sequence star located around 36 light years from Earth, the star is only 75% larger in mass and radius than our sun. Zosma
Also known as Delta Leonis, like Denebola Zosma is a white main sequence star located around 58 light years from Earth, the star has a mass and radius around twice that of the sun. Chort
Also known as Theta Leonis, along with Denebola and Zosma Chort forms the rump of Leo in the form of a bright triangle, like the two others Chort is a white main sequence star, at a distance of 165 light years from Earth it is the furthest of the trio and as a result less bright. Regulus
Also known as Alpha Leonis, Regulus is not only the brightest star in the constellation but one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Regulus is a four star system located around 80 light years from Earth, the system consists of the bright Regulus A and three dimmer stars. Regulus A is a large blue main sequence star with around 4 times the mass and radius of the sun. Algieba
Also known as Gamma Leonis, Algieba is a two star system around 130 light years from Earth, the system consists of two giant binary stars orbiting each other at a distance of around 16 billion miles (26 billion km). Adhafera
Also known as Zeta Leonis, Adhafera is a white-yellow giant star around 270 light years from Earth, it's around six times larger in diameter than the sun with around three times its mass.
Finding Leo - Northern Hemisphere
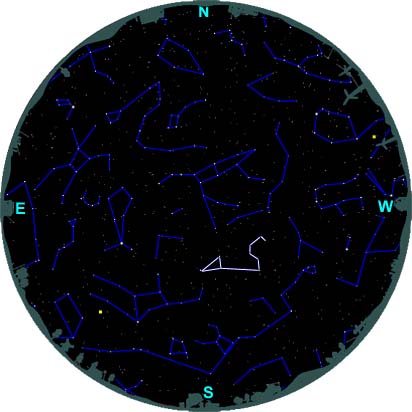
Finding Leo - Southern Hemisphere